Appearance
ESSENTIALS
Variables are key to properly utilizing bindings. So, if you haven't already, it is highly recommended to learn the basics of variables before learning about bindings:
Binding data
Binding is what transforms a static website into a dynamic, interactive application.
What is binding?
One of the reasons WeWeb is so powerful is because you can bind almost every property.
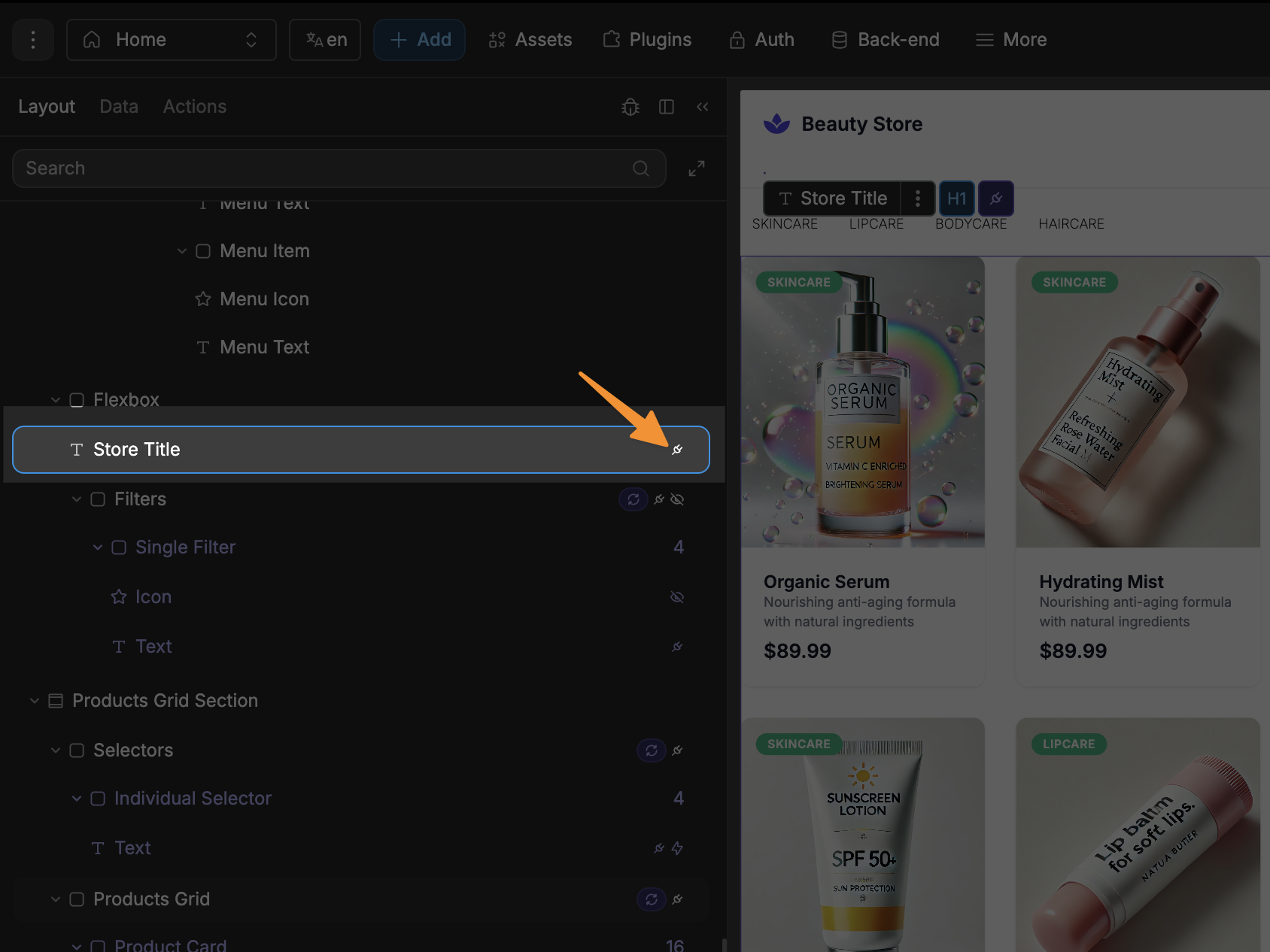
To bind a property in WeWeb, you simply need to click on the plug icon beside the property:
You will then be presented with the formula window, where you bind whatever formula or data you like:

When you bind a property, it becomes what is termed 'reactive'. This means that the property will dynamically update whenever the value returned in the binding changes.
VISUALLY IDENTIFYING BOUND PROPERTIES
Bound properties can always be identified by their purple visual appearance:

OR
You can also identify when an element has a bound property, as it will have a plug icon beside it in the layout tree:
Why is binding useful?
As mentioned at the start, binding is what transforms a static website into a dynamic, interactive application. Here's why binding is essential for your WeWeb projects:
- dynamic content display - show real-time data from your database or API directly in your app
- responsive interactions - create interfaces that adapt to user actions and data changes
- conditional UI - show or hide elements based on user permissions, data states, or other conditions
- personalization - deliver custom experiences based on user preferences or behavior
- data consistency - maintain a single source of truth across your application
For example, with binding you can:
- show a user's profile information when they log in
- display a list of products from your e-commerce database
- hide administrative features from non-admin users
- change UI styles based on user settings or app state
- validate forms as users type and show immediate feedback
Binding is the key to building fully-featured applications in WeWeb.
Binding specific property types
Different properties require specific value types when binding.
For example:
- display properties require boolean values (
trueorfalse) - style properties need appropriate units (
"300px","50%","#FF5733") - text content accepts strings, numbers, or formatted values
MATCHING THE EXPECTED FORMAT
If you are ever unsure as to what type of data you need to return in a binding, you can hover over the Expected format tooltip to see what is expected:

Binding simple data
Let's take a simple example. Let's say you want to display the current logged-in user's name in your app.
To do this, you would need to bind a text element to the name property of the user object:
CONTINUE LEARNING
Not only can binding be used to show certain pieces of data, but they can be used to conditionally change the design of elements:

